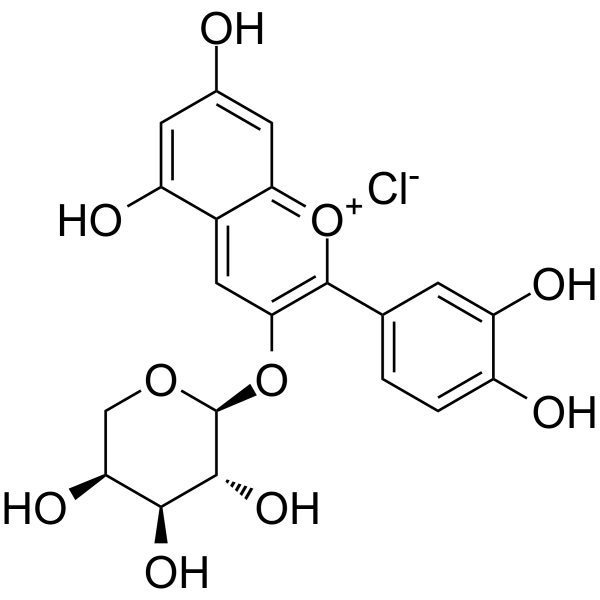
Cyanidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride
CAS No. 111613-04-8
Cyanidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride( —— )
Catalog No. M31187 CAS No. 111613-04-8
Cyanidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride has antioxidant activity. It reduces the peroxynitrite-induced suppression of mitochondrial respiration, DNA damage, PARS activation and vascular dysfunction in HUVECs.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 639 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCyanidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCyanidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride has antioxidant activity. It reduces the peroxynitrite-induced suppression of mitochondrial respiration, DNA damage, PARS activation and vascular dysfunction in HUVECs.
-
DescriptionCyanidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride has antioxidant activity. It reduces the peroxynitrite-induced suppression of mitochondrial respiration, DNA damage, PARS activation and vascular dysfunction in HUVECs.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number111613-04-8
-
Formula Weight454.8
-
Molecular FormulaC20H19ClO10
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pyranine
Pyranine is reported as a new class of fluorescent chemosensor for the Cu+ ion.
-
Mastoparan acetate(7...
Mastoparan acetate is a peptide toxin from wasp venom.
-
Eclalbasaponin I
Eclalbasaponin I has anti-oxidative, and antitumor activities, it reduces oxidative stress-induced neural cell death by autophagy activation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


